Difference between revisions of "Упражнение 4. Сериен порт (2)"
From Ilianko
| Line 278: | Line 278: | ||
== Домашна работа == | == Домашна работа == | ||
| + | Да се реализира задача 3, като се използват променливи тип stuct. | ||
| − | == | + | == Литература == |
Revision as of 09:11, 30 March 2011
Contents
Разглеждане на сигнал на сериен порт
Задача 1 Създайте програма с безкраен цикъл, която да изпраща една буква към серийния порт. Използвайте специално пригодения кабел и разгледайте осцилограмата на серийни сигнал.
structures
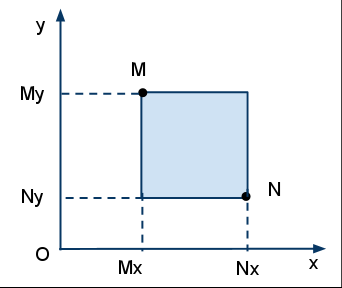
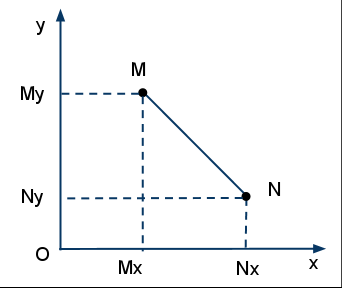
Задача 3. Да се създаде програма за намиране на лицето на квадрат по дадени координати на точки на два срещуположни върха. Координатите на точките да се въвеждат от клавиатурата, след стартиране на програмата. Първо х и у за първа точка, после x и y за втората точка.
Упътване: Напишете псевдо код на програмата на хартия, после я реализирайте.
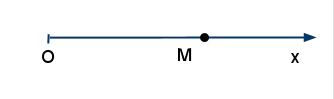
Едноизмерна точка
/* 1D Point */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x;
puts("Enter point coordinate \n");
scanf("%d",&x);
printf("The point coordinate is %i! \n", x);
return 0;
}
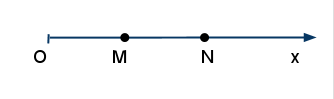
Едноизмерна отсечка
/* 1D Line */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x1;
int x2;
puts("Enter start point of line \n");
scanf("%d",&x1);
puts("Enter end point of line \n");
scanf("%d",&x2);
printf("The line is %i units long! \n", x2 - x1);
return 0;
}
Едноизмерна отсечка с struct
/* 1D Line struct */
#include <stdio.h>
struct line
{
int x1;
int x2;
};
int main()
{
struct line ln;
puts("Enter start point of line \n");
scanf("%d", &ln.x1);
puts("Enter end point of line \n");
scanf("%d", &ln.x2);
printf("The line is %i units long! \n", ln.x2 - ln.x1);
return 0;
}
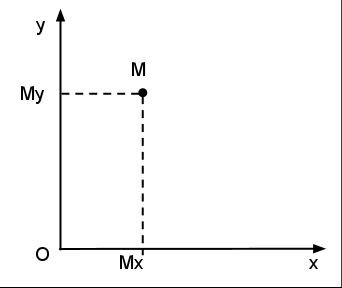
Двуизмерна точка със struct
/* 2D point struct*/
#include <stdio.h>
struct point
{
int x;
int y;
};
int main()
{
struct point pt;
puts("Enter the point X coordinate \n");
scanf("%d", &pt.x);
puts("Enter the point Y coordinate \n");
scanf("%d", &pt.y);
printf("The point coordinates are P( %i ; %i )! \n", pt.x,pt.y);
return 0;
}
Двуизмерна отсечка със struct
/* 2D Line struct */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
struct point
{
int x;
int y;
};
struct line
{
struct point x1;
struct point x2;
};
int main()
{
struct line ln;
//fisrt point
puts("Enter the start point of line X coordinate!\n");
scanf("%d", &ln.x1.y);
puts("Enter the start point of line Y coordinate! \n");
scanf("%d", &ln.x1.x);
//second point
puts("Enter the end point of line X coordinate! \n");
scanf("%d", &ln.x2.x);
puts("Enter the end point of line Y coordinate! \n");
scanf("%d", &ln.x2.y);
printf("The line is %f units long! \n", sqrt( pow(ln.x1.x - ln.x2.x, 2)+pow(ln.x1.y - ln.x2.y, 2)));
return 0;
}
Двуизмерна точка със struct и функция
/* 2D Line struct function */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
struct point
{
int x;
int y;
};
struct line
{
struct point x1;
struct point x2;
};
struct point makepoint()
{
struct point temp;
puts("Enter the point of line X coordinate!\n");
scanf("%d", &temp.x);
puts("Enter the point of line Y coordinate! \n");
scanf("%d", &temp.y);
return temp;
}
int main()
{
struct line ln;
ln.x1 = makepoint();
ln.x2 = makepoint();
printf("The line is %f units long! \n", sqrt( pow(ln.x1.x - ln.x2.x, 2)+pow(ln.x1.y - ln.x2.y, 2)));
return 0;
}
cp, mv, mkdir, rm
приемане
#include <termios.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define BAUDRATE B9600
#define MODEMDEVICE "/dev/ttyS0"
int main()
{
int fd,c, res, stop = 0;
struct termios oldtio,newtio;
char buf[255];
/* open the device to be non-blocking (read will return immediatly) */
fd = open(MODEMDEVICE, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0) {perror(MODEMDEVICE); exit(-1);}
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, FNDELAY);
tcgetattr(fd,&oldtio); /* save current port settings */
/* set new port settings for canonical input processing */
newtio.c_cflag = BAUDRATE | CRTSCTS | CS8 | CLOCAL | CREAD;
newtio.c_iflag = IGNPAR | ICRNL;
newtio.c_oflag = 0;
newtio.c_lflag = ICANON;
tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);
newtio.c_iflag &= ~(IGNBRK|BRKINT|PARMRK|ISTRIP|INLCR|IGNCR|ICRNL|IXON);
newtio.c_cflag &= ~( CRTSCTS );
newtio.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
newtio.c_lflag &= ~(ECHO|ECHONL|ICANON|ISIG|IEXTEN);
newtio.c_cflag &= ~(CSIZE|PARENB);
newtio.c_cflag |= CS8;
newtio.c_cc[VMIN]=1;
newtio.c_cc[VTIME]=0;
tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio);
/* loop while waiting for input. normally we would do something
useful here */
while ( stop == 0)
{
usleep(100);
fflush (stdout);
res = read(fd,buf,10);
// strcat(buf,buf2);
for( c=0;c<res; c=c+1)
{
if ( buf[c] == 0xd )
printf ("\n");
else
{
if (buf[c] == 0x61) { printf("ok");stop = 1;}
printf("%c", (char) buf[c]);
}
}
}
/* restore old port settings */
tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&oldtio);
return 0;
}
Домашна работа
Да се реализира задача 3, като се използват променливи тип stuct.