Difference between revisions of "Принтери (draft)"
| (58 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | == Принтери == | |
| + | |||
| + | *скорост на печат (25 ppm) | ||
| + | *цена на копие | ||
| + | *разделителна способност - (600 dpi) | ||
| + | *натоварване | ||
| + | *цветове | ||
| + | *консумативи (защитата на касетите за мастила и тонер) | ||
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Мастило струйни == | == Мастило струйни == | ||
| − | Мастило струйните принтери формират | + | Мастило струйните принтери формират цифровия образ, като изстрелват капки мастило върху хартия или друга повърхност. Този тип принтери са най-разпространените, а и самата концепция за тази технология е още от 19 век. |
| − | Първите мастило струйни принтери са от средата на миналия век, а след това започва бурното им развитие и сега се срещат както модели за домашна употреба за по-малко от 50 евро, така и специализирани машини за хиляди евро.[ | + | Първите мастило струйни принтери са от средата на миналия век, а след това започва бурното им развитие и сега се срещат както модели за домашна употреба за по-малко от 50 евро, така и специализирани машини за хиляди евро.<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inkjet_printer</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Устройството на първия мастило струен принтер е взаимствано от галванометър (механичен амперметър за малки токове). Там на мястото на стрелката е поставена дюза изстрелваща мастило върху постоянно движеща се хартия. Тази проста система все още се използва в измервателни апаратури, а първото и приложение е било в медицинта за получаване на Електрокардиограми. | ||
| + | |||
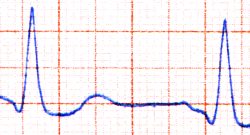
| + | [[Image:cardio.jpg|frame|right|ЕКГ]] | ||
| + | [[Image:galvan.png|frame|none|Галванометрична принтираща система]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Мастило-струйни принтери с непрекъсваема струя === | ||
| + | Споменатият по горе метод не е подходящ за възпроизвеждане на текст и графика.<ref>http://iaf.hs-heilbronn.de/wiki/Tintendrucktechnologie</ref> | ||
| + | По-голямата динамичност на принтиращата система се постигат с две промени: | ||
| + | *постоянния поток от мастило се раздробява на поток от капки от мастило. | ||
| + | *управляващата система от електро-механична се преобразува в електро-статична. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CIJexample.jpg|thumb|300px|right|Печат]] | ||
| + | [[Image:CIJ.png|frame|none|Мастило-струйни принтери с непрекъсваема струя]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Потока от мастило се раздробява на капки от пиезо вибратор. Капките се изстрелват с голяма скорост и се зареждат с различен отрицателен заряд, големината на който определя, къде ще попаднат капките. Капките със заряд се откланят към повърхността на която се печата, а останалите попадат в мастило уловителя и се рециклират. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Тези принтери имат високата скорост на печат, могат да печатат с различни по състав мастила и върху различни повърхности, а също и повърхността може да е сравнително отдалечена. Това ги прави подходящи за индустриалните маркиращи системи на всякакви опаковки. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Мастилоструйни принтери с капки по заявка === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Принтерите с непрекъснато подаване на мастило имат редица недостатъци и технологията е неприложима за компактни принтери. | ||
| + | - високо налягане, постоянно въртящ се барабан, една дюза, система рециклираща мастилото | ||
| + | |||
| + | В началото след 1970 започват интензивно да се развиват принтиращи глави с управляем във времето поток от капки и скоро се появяват се глави с пиезо-електрически модулатор. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Пиезо-модулатор ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:piezoInkHead.gif|frame|none|пиезо-модулатор]] | ||
| + | [[Image:piezoInkHead.png|frame|none|Напречен разрез на глава с пиезо-модулатор]] | ||
| + | [[Image:piezoInkHead.jpg|frame|none|Напречен разрез на глава с пиезо-модулатор]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:piezoInkHeadEpson.jpeg|frame|none|пиезо-модулатор]] | |
| − | + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_ink Твърди мастила ... xerox] | |
| − | + | ==== Термо-мастилоструйна технология ==== | |
| + | Bubble-jet Canon | ||
| + | |||
| + | HP | ||
| + | [[Image:heatInk1.png|frame|none|термо-мастилоструйна технология]] | ||
| + | [[Image:heatInk.jpeg|frame|none|термо-мастилоструйна технология]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Съществуват два вида мастила за термо струйните принтери <ref>http://www.oddparts.com/ink/faq19.htm</ref> | ||
| + | *dye-based ink - тук багрилото е изцяло разтворимо във водата, примерно, както захарта се разтваря във вода. Това прави мастилото подходящо термо главата, но в последствие, би довело до лесно обратно разтваряне във въздуха - т.е. снимката ще избелее. | ||
| + | *pigmented ink - багрилото не е напълно разтворимо, примерно както брашно във вода. При попадане върху хартията фините частици на мастилото проникват във влакнестата структура на хартията и по-трудно се отделят. | ||
== Лазерни == | == Лазерни == | ||
| + | [[Image:laser2.png|thumb|600px|none| ]] | ||
| + | [[Image:laser.png|frame|none|Фото чувствителен барабан]] | ||
| + | [[Image:laser.jpg|frame|none|лазарен принтер]] | ||
| + | [[Image:laser1.jpg|thumb|none|600px|Цветен принтер]] | ||
| + | |||
== Удърни == | == Удърни == | ||
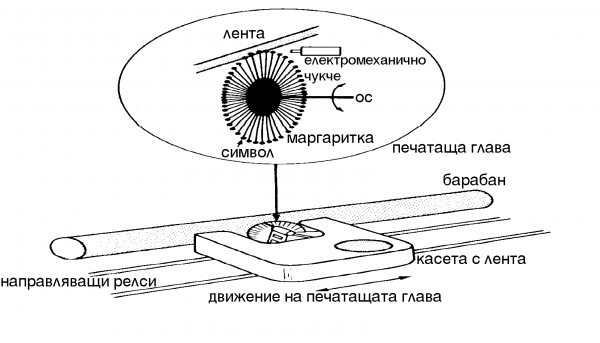
| + | === Маргариткови === | ||
| + | [[Image:DaisyWheel.jpg|Маргаритков принтер]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:DaisyWheel2.png|thumb|600px|none|Маргаритков принтер]] | ||
| + | |||
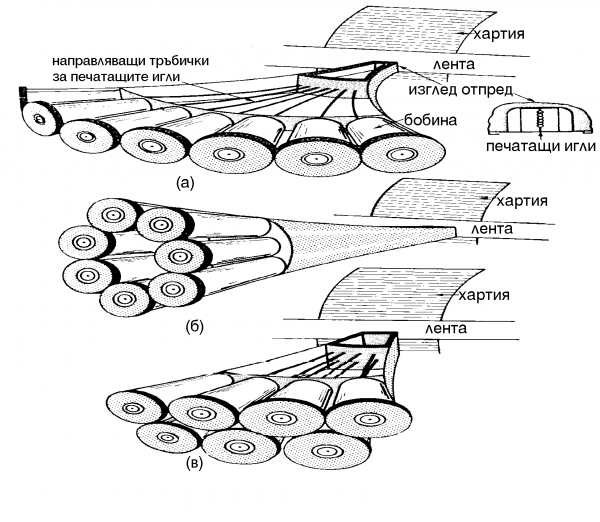
| + | === Матрични === | ||
| + | [[Image:matrix.png|thumb|600px|none|матричен принетер]] | ||
| + | ====Advantages==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dot matrix printers, like any impact printer, can print on multi-part [[stationery]] or make carbon-copies. Impact printers have one of the lowest printing costs per page. As the ink is running out, the printout gradually fades rather than suddenly stopping partway through a job. They are able to use continuous paper rather than requiring individual sheets, making them useful for data logging. They are good, reliable workhorses ideal for use in situations where printed content is more important than quality. The ink ribbon also does not easily dry out, including both the ribbon stored in the casing as well as the portion that is stretched in front of the print head; this unique property allows the dot-matrix printer to be used in environments where printer duty can be rare, for instance, as with a Fire Alarm Control Panel's output. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Disadvantages==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Impact printers create noise when the pins or typeface strike the ribbon to the paper. Sound dampening enclosures may have to be used in quiet environments. They can only print lower-resolution graphics, with limited color performance, limited quality, and lower speeds compared to non-impact printers. While they support fanfold paper with tractor holes well, single-sheet paper may have to be wound in and aligned by hand, which is relatively time-consuming, or a sheet feeder may be utilized which can have a lower paper feed reliability. When printing labels on [[release paper]], they are prone to paper jams when a print wire snags the leading edge of the label while printing at its very edge. For text-only labels (e.g., mailing labels), a [[Daisy-wheel printer|daisy wheel printer]] or [[band printer]] may offer better print quality and a lesser chance of damaging the paper. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Future of dot-matrix printers=== | ||
| + | The main use of dot-matrix printers is in areas of intensive transaction-processing systems that churn out quite a lot of printing. Many companies who might have started off with dot-matrix printers are not easily convinced to go for paperless options or printers based on other technologies because of the speed advantage of dot-matrix printers, as well as simply having many years of experience with dot matrix and being reluctant to change to a new, unproven method. | ||
| + | |||
== Термични == | == Термични == | ||
| + | Специална хартия | ||
| + | факс, касови апарати | ||
| + | A thermal printer comprises these key components: | ||
| + | Thermal head — generates heat; prints on paper | ||
| + | Platen — a rubber roller that feeds paper | ||
| + | Spring — applies pressure to the thermal head, causing it to contact the thermo-sensitive paper | ||
| + | Controller boards — for controlling the mechanism | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to print, thermo-sensitive paper is inserted between the thermal head and the platen. The printer sends an electrical current to the heating elements of the thermal head, which generate heat. The heat activates the thermo-sensitive coloring layer of the thermo-sensitive paper, which changes color where heated. Such a printing mechanism is known as a thermal system or direct system. The heating elements are usually arranged as a matrix of small closely-spaced dots—thermal printers are actually dot-matrix printers, though they are not so called. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The paper is impregnated with a solid-state mixture of a dye and a suitable matrix; a combination of a fluoran leuco dye and an octadecylphosphonic acid is an example. When the matrix is heated above its melting point, the dye reacts with the acid, shifts to its colored form, and the changed form is then conserved in metastable state when the matrix solidifies back quickly enough. See thermochromism. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Controller boards are embedded with firmware to manage the thermal printer mechanisms. The Firmware can manage multiple bar code types, graphics and logos. They enable the user to choose between different resident fonts (also including Asian fonts) and character sizes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Controller boards can drive various sensors such as paper low, paper out, door open, top of form etc., and they are available with a variety of interfaces, such as RS-232, parallel, USB and wireless. For point of sale application some boards can also control the cash drawer. | ||
| + | |||
== Термичен трансфер == | == Термичен трансфер == | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermal_transfer_printer | ||
| + | |||
== Сублимационни == | == Сублимационни == | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dye-sublimation_printer | ||
| + | |||
== Плотери == | == Плотери == | ||
== Режещи плотери == | == Режещи плотери == | ||
| Line 68: | Line 154: | ||
pigment based | pigment based | ||
sublimation | sublimation | ||
| + | ==Литература== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Компютърна периферия]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:44, 3 February 2016
Contents
Принтери
- скорост на печат (25 ppm)
- цена на копие
- разделителна способност - (600 dpi)
- натоварване
- цветове
- консумативи (защитата на касетите за мастила и тонер)
Мастило струйни
Мастило струйните принтери формират цифровия образ, като изстрелват капки мастило върху хартия или друга повърхност. Този тип принтери са най-разпространените, а и самата концепция за тази технология е още от 19 век. Първите мастило струйни принтери са от средата на миналия век, а след това започва бурното им развитие и сега се срещат както модели за домашна употреба за по-малко от 50 евро, така и специализирани машини за хиляди евро.<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inkjet_printer</ref>
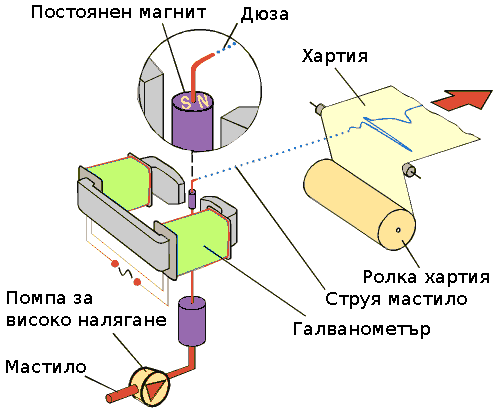
Устройството на първия мастило струен принтер е взаимствано от галванометър (механичен амперметър за малки токове). Там на мястото на стрелката е поставена дюза изстрелваща мастило върху постоянно движеща се хартия. Тази проста система все още се използва в измервателни апаратури, а първото и приложение е било в медицинта за получаване на Електрокардиограми.
Мастило-струйни принтери с непрекъсваема струя
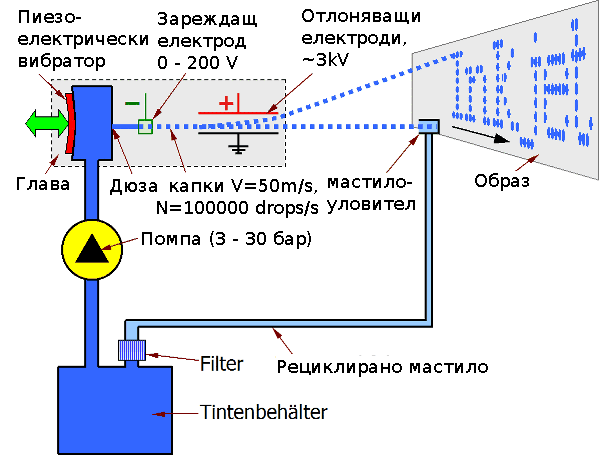
Споменатият по горе метод не е подходящ за възпроизвеждане на текст и графика.<ref>http://iaf.hs-heilbronn.de/wiki/Tintendrucktechnologie</ref> По-голямата динамичност на принтиращата система се постигат с две промени:
- постоянния поток от мастило се раздробява на поток от капки от мастило.
- управляващата система от електро-механична се преобразува в електро-статична.
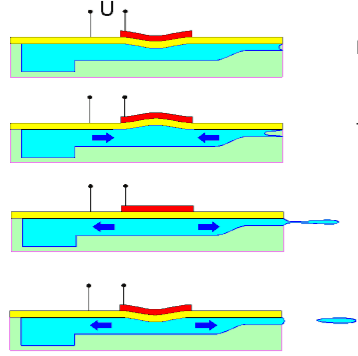
Потока от мастило се раздробява на капки от пиезо вибратор. Капките се изстрелват с голяма скорост и се зареждат с различен отрицателен заряд, големината на който определя, къде ще попаднат капките. Капките със заряд се откланят към повърхността на която се печата, а останалите попадат в мастило уловителя и се рециклират.
Тези принтери имат високата скорост на печат, могат да печатат с различни по състав мастила и върху различни повърхности, а също и повърхността може да е сравнително отдалечена. Това ги прави подходящи за индустриалните маркиращи системи на всякакви опаковки.
Мастилоструйни принтери с капки по заявка
Принтерите с непрекъснато подаване на мастило имат редица недостатъци и технологията е неприложима за компактни принтери. - високо налягане, постоянно въртящ се барабан, една дюза, система рециклираща мастилото
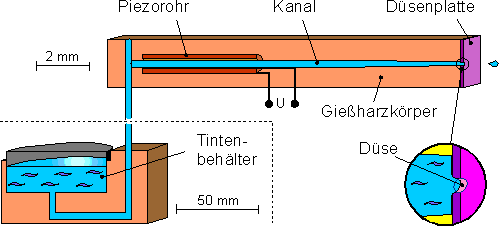
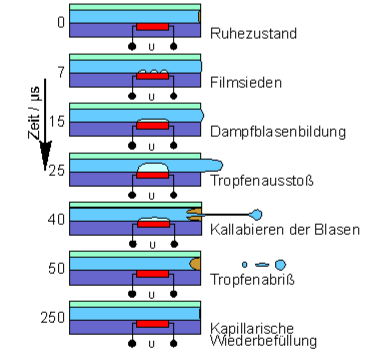
В началото след 1970 започват интензивно да се развиват принтиращи глави с управляем във времето поток от капки и скоро се появяват се глави с пиезо-електрически модулатор.
Пиезо-модулатор
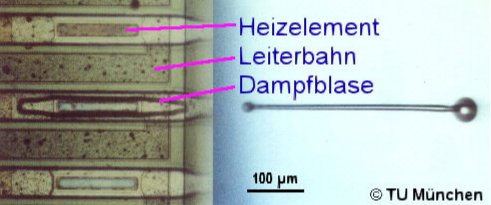
Термо-мастилоструйна технология
Bubble-jet Canon
HP
Съществуват два вида мастила за термо струйните принтери <ref>http://www.oddparts.com/ink/faq19.htm</ref>
- dye-based ink - тук багрилото е изцяло разтворимо във водата, примерно, както захарта се разтваря във вода. Това прави мастилото подходящо термо главата, но в последствие, би довело до лесно обратно разтваряне във въздуха - т.е. снимката ще избелее.
- pigmented ink - багрилото не е напълно разтворимо, примерно както брашно във вода. При попадане върху хартията фините частици на мастилото проникват във влакнестата структура на хартията и по-трудно се отделят.
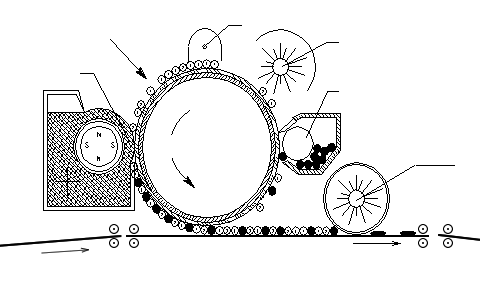
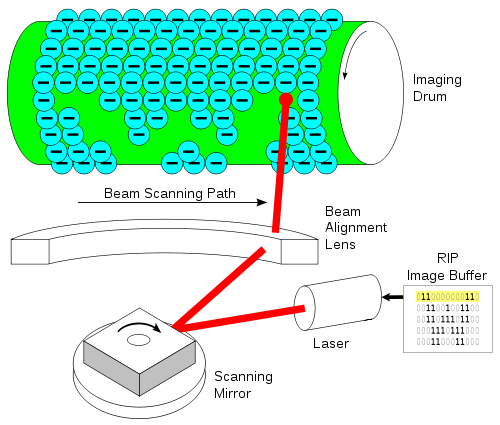
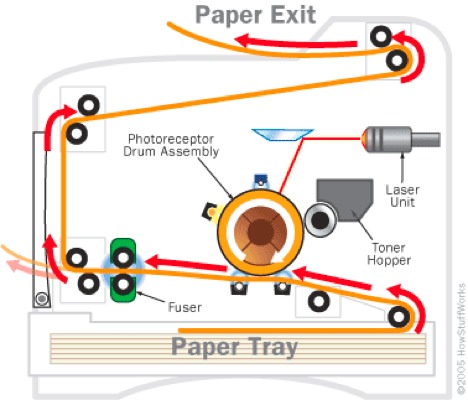
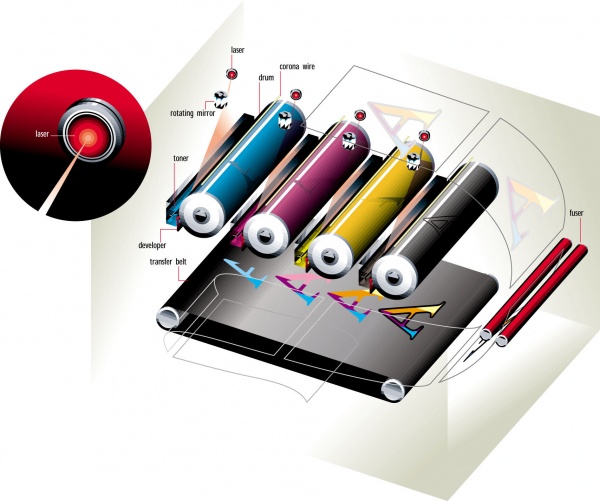
Лазерни
Удърни
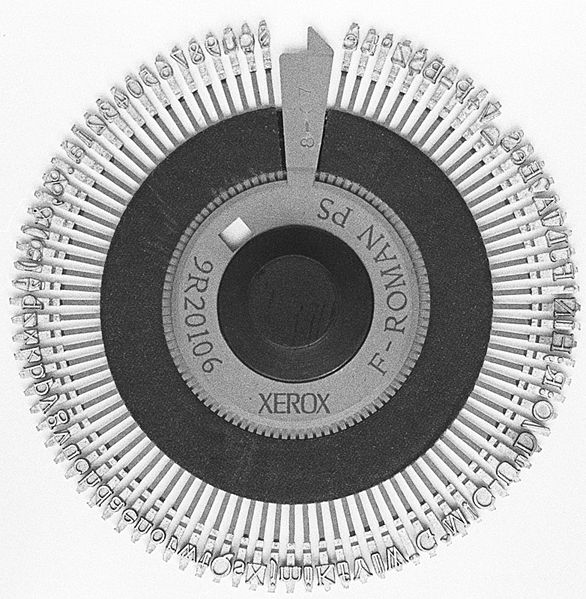
Маргариткови
Матрични
Advantages
Dot matrix printers, like any impact printer, can print on multi-part stationery or make carbon-copies. Impact printers have one of the lowest printing costs per page. As the ink is running out, the printout gradually fades rather than suddenly stopping partway through a job. They are able to use continuous paper rather than requiring individual sheets, making them useful for data logging. They are good, reliable workhorses ideal for use in situations where printed content is more important than quality. The ink ribbon also does not easily dry out, including both the ribbon stored in the casing as well as the portion that is stretched in front of the print head; this unique property allows the dot-matrix printer to be used in environments where printer duty can be rare, for instance, as with a Fire Alarm Control Panel's output.
Disadvantages
Impact printers create noise when the pins or typeface strike the ribbon to the paper. Sound dampening enclosures may have to be used in quiet environments. They can only print lower-resolution graphics, with limited color performance, limited quality, and lower speeds compared to non-impact printers. While they support fanfold paper with tractor holes well, single-sheet paper may have to be wound in and aligned by hand, which is relatively time-consuming, or a sheet feeder may be utilized which can have a lower paper feed reliability. When printing labels on release paper, they are prone to paper jams when a print wire snags the leading edge of the label while printing at its very edge. For text-only labels (e.g., mailing labels), a daisy wheel printer or band printer may offer better print quality and a lesser chance of damaging the paper.
Future of dot-matrix printers
The main use of dot-matrix printers is in areas of intensive transaction-processing systems that churn out quite a lot of printing. Many companies who might have started off with dot-matrix printers are not easily convinced to go for paperless options or printers based on other technologies because of the speed advantage of dot-matrix printers, as well as simply having many years of experience with dot matrix and being reluctant to change to a new, unproven method.
Термични
Специална хартия факс, касови апарати A thermal printer comprises these key components: Thermal head — generates heat; prints on paper Platen — a rubber roller that feeds paper Spring — applies pressure to the thermal head, causing it to contact the thermo-sensitive paper Controller boards — for controlling the mechanism
In order to print, thermo-sensitive paper is inserted between the thermal head and the platen. The printer sends an electrical current to the heating elements of the thermal head, which generate heat. The heat activates the thermo-sensitive coloring layer of the thermo-sensitive paper, which changes color where heated. Such a printing mechanism is known as a thermal system or direct system. The heating elements are usually arranged as a matrix of small closely-spaced dots—thermal printers are actually dot-matrix printers, though they are not so called.
The paper is impregnated with a solid-state mixture of a dye and a suitable matrix; a combination of a fluoran leuco dye and an octadecylphosphonic acid is an example. When the matrix is heated above its melting point, the dye reacts with the acid, shifts to its colored form, and the changed form is then conserved in metastable state when the matrix solidifies back quickly enough. See thermochromism.
Controller boards are embedded with firmware to manage the thermal printer mechanisms. The Firmware can manage multiple bar code types, graphics and logos. They enable the user to choose between different resident fonts (also including Asian fonts) and character sizes.
Controller boards can drive various sensors such as paper low, paper out, door open, top of form etc., and they are available with a variety of interfaces, such as RS-232, parallel, USB and wireless. For point of sale application some boards can also control the cash drawer.
Термичен трансфер
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermal_transfer_printer
Сублимационни
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dye-sublimation_printer
Плотери
Режещи плотери
Управление на позиционни системи
Езици за управление
2. A dye-sublimation printer (or dye-sub printer) Сублимационни принтери 3. Thermal transfer or 4. удърни – матрични, редови 5. offset печат 6. плотер 7. режещи плотери 8. управление на позиционни системи 9. езици за управление
1. Спецификация на принтер
2. скрити характеристики
Dpi
laser inkjet pigment based, dye based
impact – dot matrix
printer
Picoliters → accuracy
qualitty
cyan, magenta, yellow
plotter, cutting, ink plotter
dye based ink pigment based sublimation
Литература
<references />